Solution annealing

Annealing of inox tubes
Nowadays, you can find big price differences between the different suppliers of inox tubes. Of course the world market of inox effects prices, but the way welded tubes are produced certainly does too. Besides the price of the raw plate material and the way of welding, the applied way of annealing is of a big influence on pricing.
The way of annealing determines the corrosion resistance of the inox tube. Therefore always consider the way of annealing when you’re about to choose your tube.
The two most important and known annealing techniques that can be distinguished are:
Bright annealing
This type of production is the most frequently used and also the cheapest way of annealing.
Bright annealing can be applied by a continuous furnace or by an in-line heating coil. This often means a very short heat peak, right after the in-line welding.
The tubes are annealed using an inert gas environment. But there is no such thing as a “standard” for heating temperature or heating time. Every manufacturer is free to use his own procedures. The main concern is whether the mechanical characteristics match the applied standards
These “cheaper” tubes are often sufficient for a large variety of applications where corrosion resistance is of minor interest. But the “high frequent in-line annealing” is never enough to increase the corrosion resistance of the TIG welded part of the tube.
The welding edges of the inox strip material are TIG-welded and no additional material is added. This inevitably causes metallurgical modifications. The structure of the welding seam lies in a dendritical structure in contrary to the globulare structure of the strip base material. During recooling of the welding seam, an analytical segregation occurs. The concentration chromium may be reduced with about 10% and the concentration of molybdanium may even be reduced with up to 50%. These segregations are based on physical mechanisms and appear regardless the manufacturer.
Because of this mechanisms the corrosion resistance in the welding area is lower than the surrounding base material.
Cold working the welding seam on the interior is the first step to recristallisation of the welding area. By annealing the process of recristallisation is fulfilled. Thereby the segregated alloy parts chromium and molybdanium defund back in their hereditary atomium position and a recristallised, globular, austenitical structure is reformed.
The standard in-line annealing method however, may be insufficiënt when certain corrosive substances are used.
Solution Annealing
It may be better to use the application of solution annealing.
Solution annealing implies that the tubes are treated with a temperature of at least 1080°C and a sufficient heating time (minutes). The applied temperature and and heating time are inherently linked to the inox gradation. A short recooling time is necessary. After the solution annealing treatment, the welding seam area almost has the same corrosion resistant characteristics as the surrounding base material.
Solution annealing nowadays is done by using a continuous electrical or a batch type oven. This implies a high investment and requires quite a lot of maintenance. The tubes also have to be re-straightened after the solution annealing treatment.
A TIG-welded tube, submissed to solution annealing, shows an almost equal corrosion resistance as the base strip material. This was also concluded after research in laboratories.
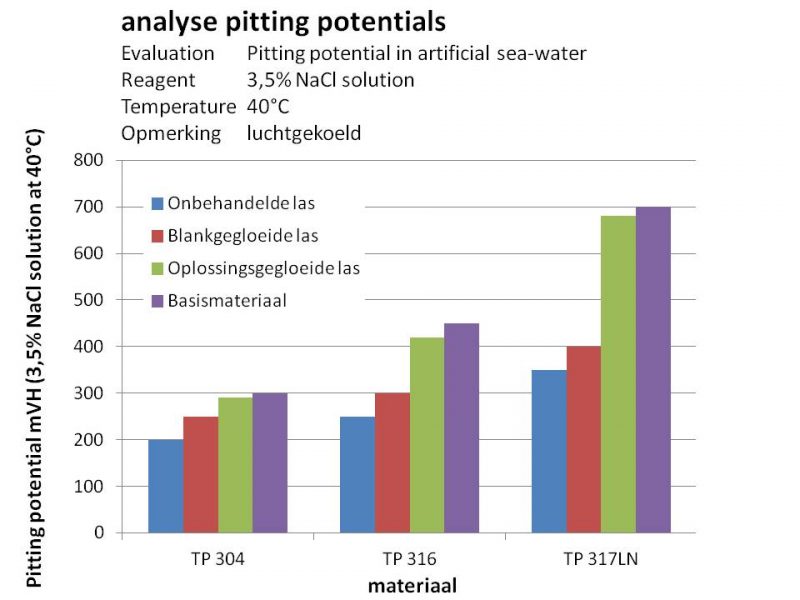
Corrosion resistance
The following graphic shows the different corrosion resistance potentials, in relation to pitting corrosion.
The higher the percentage chromium and molybdanium, the larger the differences in corrosion resistance. It shows clearly that, even when one chooses a more expensive alloy, the final way of annealing determines the corrosion resistance of the tube.
Share this: